|
|
本帖最后由 morning 于 2011-5-26 23:29 编辑
选自著名的地球化学刊物《地球化学与宇宙化学学报》(Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta)2011
研究发现二叠-三叠纪大火事件证据
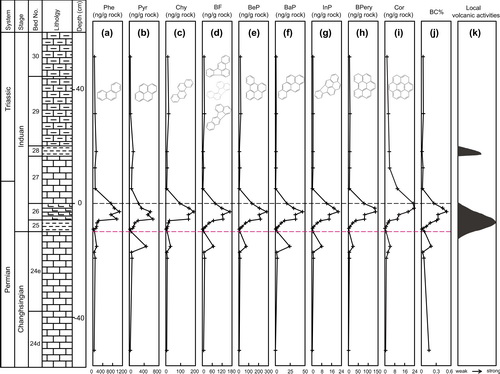 
图1 燃烧源多环芳烃和黑碳在煤山剖面P/Tr界线地层的分布
二叠纪末期地表环境发生了重大变化,出现了地质历史上规模最大的生物灭绝事件。针对这次生物灭绝事件,研究者提出了很多假说,但由于地质记录的不完整以及解释的不确定性,对当时的地球环境变化以及生物灭绝的原因等问题一直没有定论。
从图1清晰地看出,3环的菲(Phe)到7环的晕苯(Cor),以及黑碳(BC)在界线地层(26层)呈现高的峰值,暗示了当时发生了大火事件,大火发生在煤山附近强烈的火山活动期间。
中科院地质与地球物理研究所博士后沈文杰与合作导师林杨挺研究员等人在对浙江煤山剖面的研究过程中发现了大量的燃烧源多环芳烃(PAHs)和各种不同尺寸的黑碳(BC),这些物质在事件层(25-26层)呈现极高的峰值。PAHs和BC是含碳物质燃烧之后的产物,据此他们首次明确提出了二叠-三叠纪之交大火事件的假说。图1中红色短线为生物灭绝线,沿这条线识别出了陆地大火、海洋缺氧、强烈的火山活动和生物灭绝等重大地质事件。
高分辨率地层显示,大火事件与海洋缺氧、强烈的火山活动及生物大规模灭绝几乎同时发生,表明它们之间有直接的成因联系。大火为陆地上发生的事件,可能指示了陆地生物的大规模灭绝(但不可能是陆地生物大规模灭绝的根本原因),而强烈的火山活动可能是二叠-三叠纪之交环境巨变和生物灭绝的根本原因。
(来源:中科院地质与地球物理研究所)
Evidence for wildfire in the Meishan section and implications for Permian–Triassic events
Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and black carbon (BC) in sediments are powerful tools in the identification of the combustion process throughout geologic history. In this study, combustion-derived PAHs and BC were carefully investigated in sediments from the Global Stratotype Section and Point of the Permian-Triassic (P/Tr) boundary in Meishan, China. Quantitative analyses of combustion-derived PAHs and BC demonstrate anomalously high concentrations in the boundary event beds that coincide with the mass extinction horizon. The prevalence of parent polynuclear aromatics (e.g., phenanthrene) in PAHs, together with non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis, confirms that the PAHs are mainly derived from vegetation burning instead of having a coal and/or oil origin. BC detected in sediment occurs in various forms from large irregular charcoal particles to fine aciniform soot, with an equivalent reflectance of up to 3.5%. The results strongly suggest that a wildfire occurred during the P/Tr boundary, which served as one of the possible triggers of mass extinction on land. The wildfire occurrence indicates that the O2 concentration of the atmosphere during (or before) the P/Tr mass extinction was probably >17%. The temporal coincidence of the mass extinction with intensive volcanic eruption, marine anoxia and wildfire events in the region of the Meishan section provides new insight into the mechanisms of the P/Tr biotic crisis. Our results show that wildfires could have played an important role in the collapse of the ecosystem in the Meishan P/Tr events.
|
|